Application of Stainless Steel Deep Drawing Oil in Spinning Process
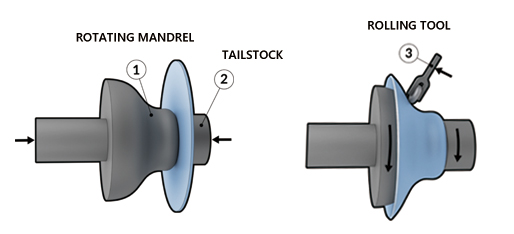
The spinning process typically involves clamping a metal sheet onto a spinning lathe, where the spindle drives the blank and mandrel to rotate together. A roller then applies pressure to the rotating blank, causing local plastic deformation, which gradually spreads across the entire blank, forming various hollow rotational parts.
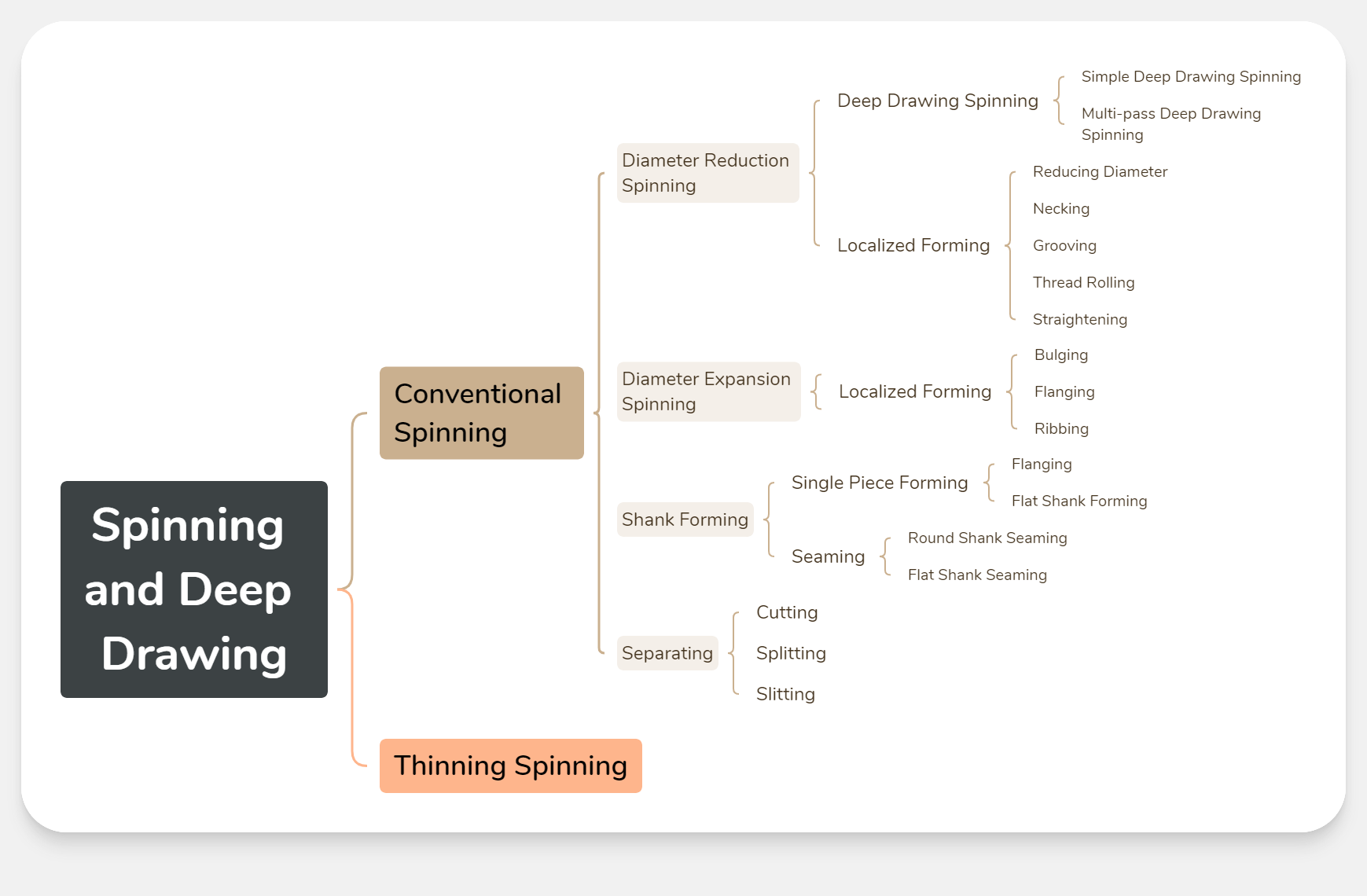
1.Classification and Characteristics of Spinning Process
The spinning process can be classified into several types:
- Deep drawing spinning
- Shear spinning (conical thinning spinning)
- Cylindrical thinning spinning
- Necking, bulging, trimming
- Flanging, internal flanging
- Corrugating or beading
- Surface finishing
|
Classified by Process |
|---|
|
|
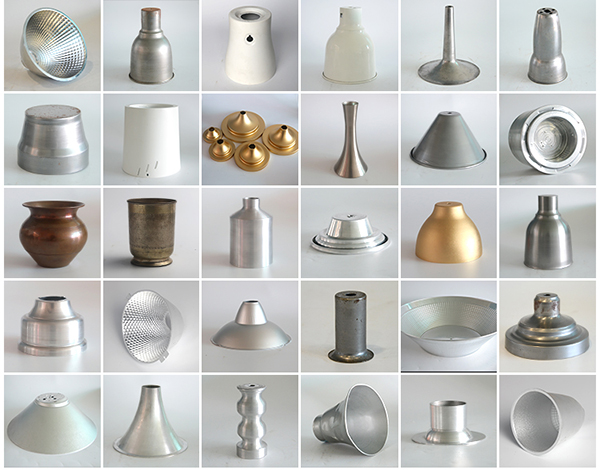
Spinning can form workpieces such as cylindrical, conical, paraboloid, and other curved rotational bodies. The process is widely applicable, especially for producing rotational workpieces. However, due to its lower production efficiency, spinning is more suitable for trial production and small-batch manufacturing. When production exceeds 1,000 pieces, the cost of spinning parts may surpass that of stamped parts.
2. Materials and Applications of Spinning
The spinning process is suitable for a variety of metal materials, including:
- Carbon steel
- Aluminum, aluminum alloys
- Stainless steel
- Copper, brass
- Silver
- Nickel alloys
- Hard-to-deform metals like titanium, molybdenum, tungsten, tantalum, and niobium
Among these, carbon steel, aluminum, and stainless steel account for the largest proportion, making up over 80% of the total processed materials.
|
Some Spinning Process Products |
|---|
|
|
3.Production Principles and Lubrication Process
|
CNC Spinning Machine |
Spinning Process Diagram |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Spinning Process Principle Video
Lubrication and cooling are critical in the spinning process. Commonly used lubricants include:
- Machine oil
- Soap
- Paraffin
- Grease
- Blended oil
- Water-soluble oil
- Sprays
- Gelled zinc
- Molybdenum disulfide
In ordinary spinning, where the roller contacts the workpiece in a rotational manner, fluid lubrication is generally sufficient, and the lubrication requirements are not stringent. However, in thinning spinning, lubricants are frequently used to reduce deformation resistance and improve surface quality.
Points to Note
- When using fluid lubricants, the contact between the blank and roller is rolling, making it easier for the lubricant to enter the contact surface.
- The higher the lubricant viscosity, the higher the blank's rotational speed, the larger the roller diameter, and the smaller the roller feed rate and spinning pressure, the better the lubrication effect.
- Lubricants should be applied evenly to prevent surface patterns on the product.
4.Customer Production Situation
The customer manufactures stainless steel products with a material thickness of 0.8mm and a drawing depth of 160mm. The lubricant is applied manually.
Production Situation
Problem Analysis
- The ordinary machine oil has limited lubrication, resulting in surface scratches on the product.
- Some oils have low viscosity, causing them to be flung off during high-speed rotation of the mandrel.
- Oils with high viscosity are difficult to apply evenly, affecting product quality.
5.Solution
Given that the customer's original oil had low viscosity and limited lubrication, requiring six applications during the process, the company recommended a more suitable product in terms of viscosity and lubrication (Stainless Steel Deep Drawing Oil Form DP 50) based on customer feedback.
6.Results
The customer's original oil required six applications throughout the process, while the new company-recommended oil only required 1-2 applications. Product inspections every 200 pieces showed dimensional tolerances within 0.2mm, meeting the required standards.